Healthcare is perpetually conflicted by challenges in achieving the quadruple aim of reducing costs, improving population health and health equity, improving the patient experience, and improving the work-life balance of healthcare professionals. Particularly in radiology, administrators have prioritized efficiency improvements to help alleviate these challenges. Industry leaders such as GE HealthCare are working on advanced radiology technologies with digitization and solutions based on artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize clinical workflows and productivity, elevate the patient experience, increase access, and reduce costs.
Advanced radiology technology can enable fast image acquisition and high image quality as well as enhance the patient experience. These innovations, applied across clinical specialties, contribute to improving workflows and diagnostic accuracy and can lead to a faster diagnosis. Advances in imaging have also influenced the expansion of minimally invasive surgical techniques and reduced the need for open procedures, reducing risk and patient recovery times.[1] In a growing area of advanced imaging and interventional radiology, industry experts predict market growth for minimally invasive procedures to reach $94.42 billion by 2030.[2],[3]
Evolving the field of interventional radiology
Not only have traditional surgeries become more precise with advanced imaging technologies, but numerous new minimally invasive procedures have been developed, enabled by advanced imaging and embedded AI tools.[4]
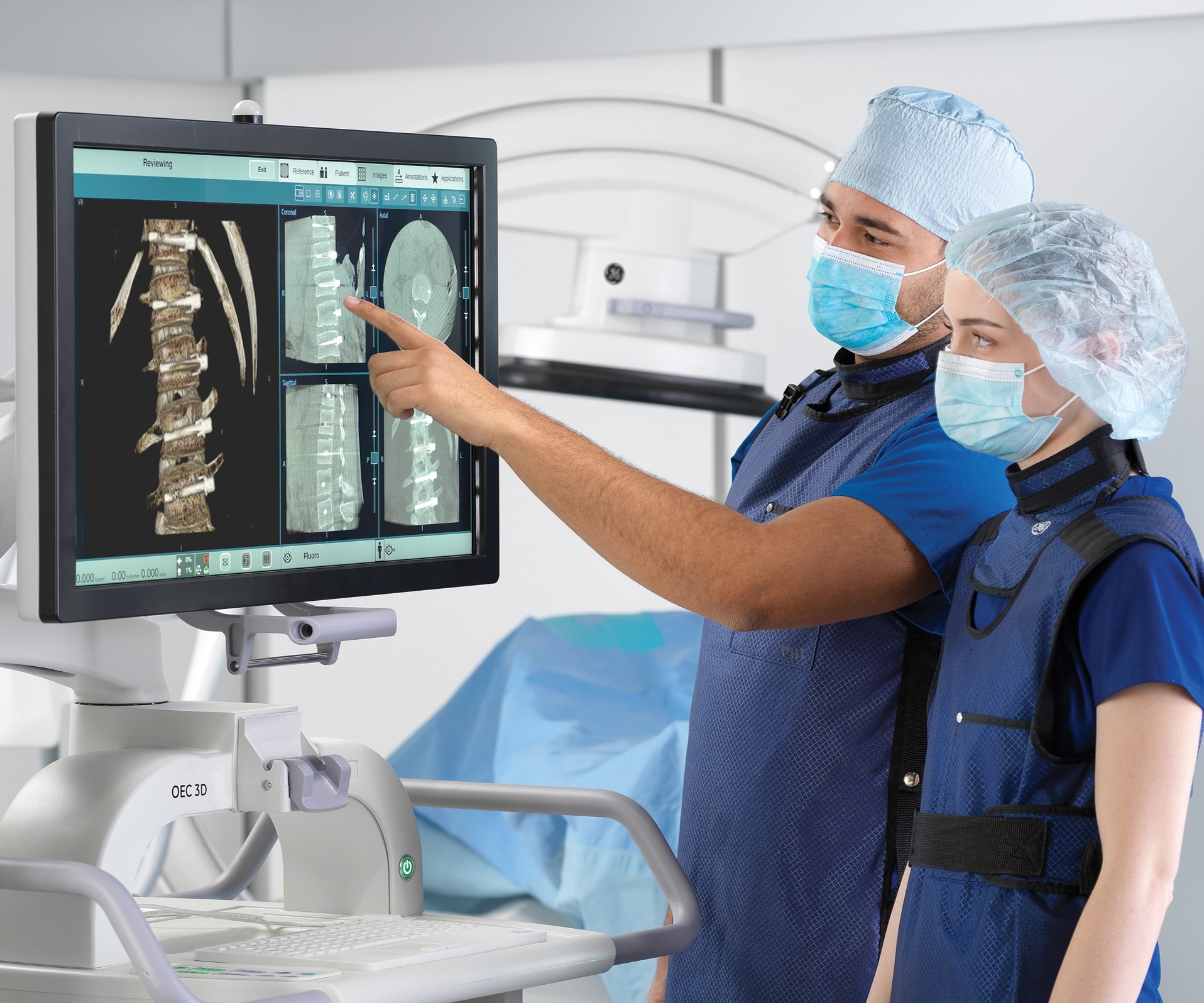
Innovative interventional image-guided systems are helping providers meet the increasing demand by revolutionizing image-guided therapies and improving clinical workflows and accuracy in the interventional radiology suite. Ergonomically designed systems provide improved logistical access to patients and workspace flexibility. Thoughtfully placed monitors ensure easily accessible visibility of diagnostic images and can highlight even the slightest difference in tissues and cells for clinicians, ensuring safety and accuracy and potentially leading to quicker surgeries.
“We’re investing in digital imaging technologies supported by intelligent systems and devices to enable clinicians’ access to all relevant information at the point of care,” said Philip Rackliffe, president and CEO of GE HealthCare’s image-guided systems. “New technologies in the interventional suite, such as augmented imaging and AI tools, enable clinicians to clearly focus on the patient and the procedure, performing minimally invasive surgeries and therapies with increased precision and accuracy.”
Accommodating variability of interventional radiology procedures
Patient preference for minimally invasive procedures is based on quicker recovery times, fewer complications, smaller incisions, reduced scarring and pain, improved outcomes, and shorter hospital stays.[5] Some procedures can even be performed on an outpatient basis. Payers also value these benefits and the lower cost of minimally invasive procedures versus conventional in-patient surgeries.[6]
To manage the increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures, many hospitals are integrating interventional solutions where they can co-locate operating rooms (ORs), hybrid ORs, medical imaging, procedure rooms, and other specialty rooms.[7] These new spaces are typically equipped with the latest interventional devices, robotic surgical equipment, and medical imaging equipment, which is used frequently during these types of procedures.
Integrated surgical suites are suited to help streamline workflows, spanning multiple departments that share the space, including prep, recovery, and accommodating for multiple procedure types. This approach, as opposed to having a dedicated space for each procedure type, is an evolution in innovative healthcare.
The variability of procedure types requires the need for suites with ergonomic workspaces, which are often shared by clinicians from different specialties. It is critical to have optimal monitor placement and visualization tools to support diverse clinical setups for different procedures. Additionally, streamlining the procedure with the ability to access all patients for intraoperative imaging is also imperative. Integrating solutions into the setup and during the procedure can provide a holistic approach to solving workflow challenges, such as a robotic mobile gantry that is easy to move and operate along with enabling the clinicians to have access to real-time images for immediate attention. Advanced applications continue to help elevate workflow efficiency as well as deliver increased clinical insights to help drive improved patient outcomes.
Advancing minimally invasive surgeries with AI and augmented imaging
Minimally invasive procedures in interventional radiology are supported by innovative, intelligent systems and devices. AI tools are integrated as smart assistants that provide real-time support to clinicians during interventional procedures, helping them aggregate and derive meaningful insights from the complex data they need to access during each procedure.
Robot-assisted surgery is also becoming more commonplace in the OR.[8] Robotic devices are frequently used to assist in cardiac valve repair, prostatectomies, and gynecological surgical procedures.[9] Another exciting area in image-guided therapy that has tremendous potential is augmented reality. Augmented reality offers clinicians increased flexibility to move around the patient during a procedure while still having all relevant patient information in their direct line of sight.
GE HealthCare is partnering to help surgeons see patients’ anatomies more realistically as a 3D holographic image with the help of augmented reality goggles. Using this tool, the clinician does not have to turn away from the patient to review an image on the monitor, and with additional collaboration tools, the clinician can share the image and confer with peers or referring physicians.
Encouraging innovation with an open ecosystem for development
Minimally invasive procedures offer the opportunity for clinicians to perform procedures for serious conditions such as pulmonary embolisms, deep vein thrombosis, and a variety of structural heart valve issues. During these interventions, multiple image acquisitions are often necessary to analyze complex vasculature, and sophisticated software tools have been developed to assist clinicians’ accurate execution of the procedure. For example, a 3D visualization software solution is designed to help clinicians simulate injections of the embolic agent dynamically for advanced vasculature visualization so they can perform minimally invasive embolization procedures with confidence.
Many new dynamic tools that support these types of complex procedures continue to be developed. As a developer and leader in the healthcare and AI space, GE HealthCare created a digital health platform designed to accelerate application integration by connecting devices and other data sources into an aggregated clinical data layer. This platform enables broad-scale adoption and access by clinicians who can utilize these innovations to aid in a complex procedure or diagnosis. Through open and published interfaces, healthcare providers and third-party developers can partner to seamlessly deploy their applications, with the platform supporting the integration of the applications into existing workflows.
Building a new perspective in image-guided therapies
Throughout the healthcare industry and within radiology, it continues to be necessary to create efficiencies wherever possible to keep pace with increased demand while improving outcomes and controlling costs. Evolving innovation and integration into health systems will be key, especially in specialty-focused areas such as surgical procedures, to reduce risk, minimize costs, and improve accuracy.
As an industry leader in imaging, GE HealthCare rises to the challenge of helping clinicians deliver care with no limits, today and tomorrow. While enabling precision health, advanced imaging and image-guided systems continue to support clinicians with solutions for improving efficiency and clinical outcomes.
RELATED CONTENT
View on-demand keynote presentations:
DISCLAIMER
Not all products or features are available in all geographies. Check with your local GE HealthCare representative for availability in your country.
REFERENCES
[1] Haigron P, Luo L, Coatrieux JL. Issues in image-guided therapy. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine. July-August 2009;28(4):96-98. doi: 10.1109/MEMB.2009.932895.
[2] Patients’ preference for minimally invasive surgery market to rise with new devices and benefits. BioSpace. Published April 8, 2022. https://www.biospace.com/article/patients-preference-for-minimally-invasive-surgery-market-to-rise-with-new-devices-and-benefits/. Accessed March 17, 2023.
[3] Linu D, Onkar S. Minimally invasive surgery market by service type (laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery), condition (gastrointestinal conditions, spinal conditions, gynecologic conditions, and other conditions), and end user (hospitals & clinics and ambulatory surgical centers): Global opportunity analysis and industry forecast, 2021-2030. Allied Market Research. October 2021. https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/request-sample/2585.
[4] What is image-guided therapy? Brigham and Women’s Hospital. https://www.brighamandwomens.org/research/amigo/image-guided-therapy-at-bwh. Accessed March 17, 2023.
[5] Narain AS, Hijji FY, Duhancioglu G, et al. Patient perceptions of minimally invasive versus open spine surgery. Clinical Spine Surgery. April 2018;31(3):E184-E192. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000618.
[6] Minimally invasive surgical instruments market size, share & trends analysis report by device (handheld instruments, inflation devices), by application (cardiac, gastrointestinal), by end use, and segment forecasts, 2022-2030. Grand View Research. https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/minimally-invasive-surgical-instruments-market.
[7] Interventional platform integrates ORs, procedure rooms and imaging. Stanford Medicine. https://stanfordhealthcare.org/health-care-professionals/medical-staff/medstaff-update/2019-september/interventional-platform-integrates-ors-procedure-rooms-and-imaging.html. Accessed March 17, 2023.
[8] Sheetz KH, Claflin J, Dimick JB. Trends in the adoption of robotic surgery for common surgical procedures. JAMA Network Open. January 2020;3(1):e1918911. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.18911.
[9] Kuzma C. 7 common robotic surgeries. Healthgrades. Last updated July 9, 2021. https://www.healthgrades.com/right-care/tests-and-procedures/7-common-robotic-surgeries. Accessed March 17, 2023.